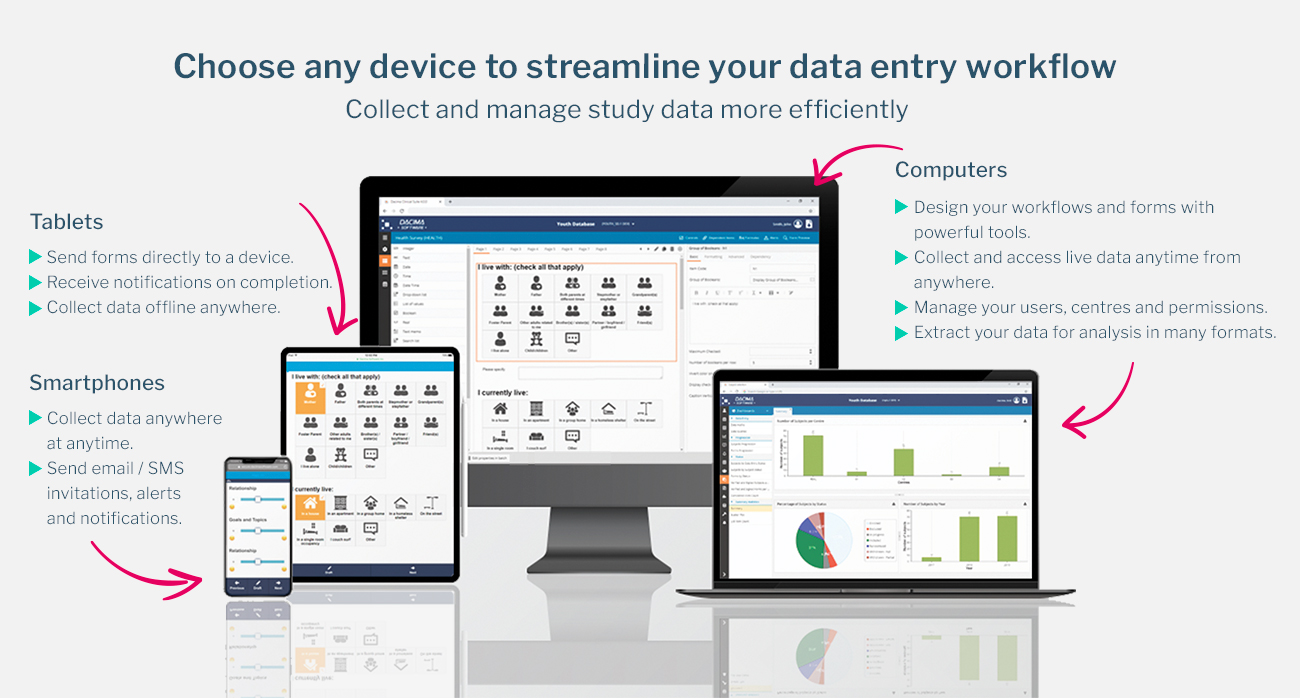
In modern research and field operations, reliable data collection tools are essential for maintaining accuracy and efficiency. Many research environments operate in locations where internet connectivity is limited or inconsistent. In such situations, Offline EDC provides a powerful solution that allows data to be collected digitally without requiring a constant network connection. This approach ensures that information can still be recorded, stored, and later synchronized once connectivity becomes available.
Field researchers, healthcare professionals, and survey teams often work in remote areas where online systems may fail due to poor infrastructure. Traditional paper-based documentation once served as the only alternative, but it introduced numerous challenges such as transcription errors, lost forms, and delayed data processing. Offline digital tools have transformed this process by enabling data entry directly into secure digital systems that function independently of internet access.
Offline data capture tools allow users to collect information using mobile devices, tablets, or laptops. Data is securely stored on the device and automatically synchronized with central databases once a connection is restored. This workflow ensures continuity in research operations without interrupting fieldwork activities.
The Growing Importance of Digital Data Capture
Digital transformation has significantly influenced how organizations manage information. Research institutions, clinical trial teams, and public health organizations increasingly rely on electronic data capture systems to streamline workflows. These systems allow teams to replace manual paperwork with structured digital forms that improve accuracy and consistency.
One major advantage of digital systems is real-time validation. Data entry tools can immediately detect incomplete fields or inconsistent responses, allowing users to correct errors before submitting records. This reduces the need for time-consuming data cleaning processes later.
Another benefit is improved organization. Digital platforms automatically structure data into standardized formats, making it easier to analyze and manage large datasets. This is particularly valuable for large-scale studies that involve thousands of participants or survey responses.
For field-based research, the ability to collect data offline is particularly valuable. When teams are able to capture information without relying on internet access, they can continue working efficiently regardless of location.
How Offline Data Systems Work
Offline data systems are designed to function independently from continuous connectivity. Data collection applications are installed directly on mobile devices, allowing users to access forms and surveys even when offline.
During fieldwork, users enter responses into digital forms. These forms often include validation rules that prevent incorrect entries. The collected data is stored securely within the device’s local storage.
Once the device reconnects to the internet, the system synchronizes the stored data with a central database. This synchronization process ensures that all collected records are safely transferred and integrated into the main data system.
The use of Offline Electronic Data Capture significantly improves workflow reliability. Teams no longer need to delay work while waiting for internet access. Instead, they can focus on collecting high-quality data and upload it when connectivity becomes available.
Advantages of Offline Data Collection
Offline data capture offers several important advantages for organizations operating in challenging environments. One of the most significant benefits is uninterrupted productivity. Field teams can continue collecting data regardless of network conditions.
Accuracy is another major advantage. Digital forms reduce transcription errors because information is entered directly into the system rather than being copied from paper documents. Built-in validation rules further enhance accuracy by preventing incomplete or inconsistent entries.
Data security also improves with digital systems. Information can be encrypted and stored securely within the device, protecting sensitive records until they are transferred to the main database.
Another benefit is faster data availability. Once synchronization occurs, collected information becomes immediately accessible to central teams. This allows researchers and analysts to begin reviewing results sooner than with traditional paper-based workflows.
Applications Across Multiple Industries
Offline data capture tools are widely used across many industries that rely on field-based operations. In healthcare research, clinical trial teams often conduct studies in remote areas where internet connectivity is unreliable. Offline systems allow them to collect patient information and research data efficiently.
Public health initiatives also benefit from offline data capture. Health workers conducting surveys or vaccination campaigns can record information during field visits without worrying about connectivity issues.
Environmental research teams frequently operate in forests, mountains, and other remote locations. Offline digital tools allow them to document observations, measurements, and survey results without carrying stacks of paper forms.
Agricultural studies and community development programs also rely on offline data systems to gather accurate information from rural populations. By reducing logistical challenges, these tools enable more efficient research operations.
Challenges and Considerations
While offline data systems offer many benefits, organizations must also consider certain challenges. Device management is an important factor, as field teams must ensure that mobile devices are properly maintained and charged during extended fieldwork.
Data synchronization processes must also be carefully designed to prevent duplicate records or conflicts. Reliable software platforms include safeguards that ensure smooth and accurate synchronization.
Training is another key consideration. Field teams should receive proper guidance on how to use digital forms, manage devices, and follow data security protocols. Proper training ensures that technology is used effectively and consistently.
Despite these considerations, the advantages of offline data systems far outweigh the challenges when implemented correctly.
Key Features of Effective Offline Data Capture Systems
-
Ability to collect data without internet connectivity
-
Secure local storage on mobile devices
-
Automatic synchronization when connection is restored
-
Data validation rules to prevent entry errors
-
Encryption for protecting sensitive information
-
Structured digital forms for standardized data collection
-
Integration with central databases and analytics platforms
-
Audit trails for tracking changes and updates
-
Compatibility with multiple devices and operating systems
-
User-friendly interfaces for field teams
Elements of Successful Offline Data Systems
1. Reliable Local Data Storage
Offline data systems must securely store collected information on the device until synchronization occurs. This storage must protect data from accidental deletion, corruption, or unauthorized access. Encryption and secure storage methods help ensure that sensitive information remains protected during fieldwork.
2. Structured Digital Forms
Well-designed digital forms improve the accuracy and consistency of collected data. Forms should include clear labels, logical field structures, and validation rules that guide users through the data entry process. These features reduce errors and improve overall data quality.
3. Efficient Synchronization Processes
Once internet connectivity becomes available, collected data must synchronize quickly and accurately with the central database. Efficient synchronization ensures that records are transferred without duplication or data conflicts, maintaining the integrity of the dataset.
4. User-Friendly Interface
Field teams often work under challenging conditions, so data collection tools must be easy to use. Intuitive interfaces, clear navigation, and simple data entry workflows allow users to focus on their work rather than struggling with complex technology.
5. Strong Data Security Measures
Protecting sensitive data is critical in any research or field operation. Secure authentication, encrypted storage, and controlled access permissions help maintain data privacy while ensuring that only authorized personnel can access collected records.
As digital technologies continue to evolve, reliable data capture systems will play an increasingly important role in research and field operations. By enabling teams to collect information in remote environments without relying on internet connectivity, offline solutions improve efficiency, accuracy, and overall data quality.
Organizations that adopt modern data capture strategies benefit from faster workflows, improved data management, and stronger compliance with research standards. With the continued advancement of tools supporting Offline Electronic Data Capture, field-based research will become even more efficient and accessible in the future.
Dacima Software